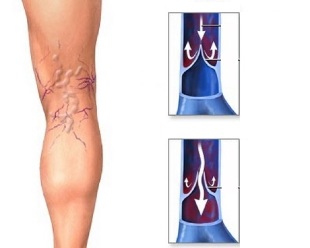
Varicose veins (varices) is one of the most common and oldest diseases of the vascular system, which has opened since the time of ancient Egypt. With the help of the Egyptian papyri and the excavation was found a mummy with signs of varicose veins. The disease interested the famous and ancient doctors: Hippocrates, Galen, and Avicenna, and later Troyanova, Trendelenburg. IDO still the disease has not lost its importance in modern medicine. Definition of "Varicose" comes from the Latin word "varix", which means "extension", therefore, the disease is called "Varicose veins." This disease is characterized by expansion and increasing the length of the peripheral veins in serpentine tortuosity (deformations), as well as a violation of the outflow of blood on them, the resulting valve insufficiency and the weakening of their walls. The disease most often affects the veins of the lower extremities, as the main burden of the outflow of blood (large volume) falls on them, therefore, preferred this section. Varicose veins occurs in about 17 - 25% of the population. At a young age the disease occurs equally in boys and girls. At the ripe age of women will be sick 2 - 3 times more often than men, due to hormonal changes the female body (menstruation, pregnancy, menopause).
Causes and risk factors in the development of varicose veins
The exact cause of the disease is not known, we only know that under the influence of some factors is developing weakening of the valves, the pressure increase and loss of elasticity of the walls of the superficial and connecting veins. Risk factors:
- Genetic predisposition: the transfer of varicose veins by inheritance is caused by mutation of the gene responsible for the structure of the vessel wall, the result of the mutation, children are born with congenital weakness of the connective or muscular tissue of the vessel wall, or lack of it of the valve (negative number), and as a consequence there is a weakness of the vessel wall and increased pressure in the veins.
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause): pregnancy changes the hormonal makeup of an organism (increasing the level of progesterone and decrease of estrogen) that affect the formation of clotting factors (increase them) to reduce the tone of the venous wall (as a result of destruction of collagen and elastic fibers of the vessel wall) all this leads to the formation of blood clots, blockage of blood vessels and their deformation.
- Obesity : excess weight leads to a sedentary lifestyle, which is a slowdown in circulation, plus excess fat increases intra-abdominal pressure, which violates the outflow of blood through the veins, resulting in the development of stagnation in the veins and the possible development of the disease.
- Diabetes :chronic elevated levels of blood sugar over time damages blood vessels, which is a favorable environment for the development of blood clots.
- Alcohol abuse : excessive alcohol consumption leads to dehydration and thickening of the blood, formed as a result of blood clots that clog veins and compromises blood flow.
- Weight lifting (movers),long walking or long standing work (sellers, conductors): associated with a decrease in muscle tone, increased intra-abdominal pressure and, as a consequence, slowing down and obstruction of blood flow to the heart and the development of its stagnation in the lower extremities.
- Congenital coagulation defects: congenital hypercoagulation (excessive production of clotting factors in the blood) leads to the formation of blood clots and disruption of the blood through the vessels.
- Poor nutrition: a lack of certain vitamins in the diet (Vit.C, E, R, plant fibers play a role in strengthening the vessel wall and improve blood circulation).
- Wearing tight underwear: his constant wearing causes mechanical compression of the veins, causing obstruction of the venous outflow from the lower extremities.
- Chronic constipation : frequent increase in abdominal pressure (during exertion) leads to difficulty of outflow of blood from the lower extremities.
- Frequent walking high heel: lack of movement of leg muscles and the development of stagnation.
- Hot season: frequent thirst leads to dehydration of the organism occurs blood clots and blood clots.
- Concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system or diseases of the kidneys: impaired outflow of venous blood (heart valve insufficiency, congenital defects).
- Overdose of the drugs increasing blood coagulation: risk of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
- Surgery a loss of some volume of blood is not a comfortable position on the operating table (the compression of certain blood vessels), leading to the risk of blood clots.
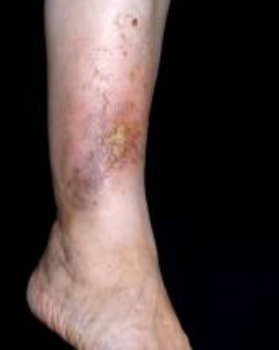
Complications of varicose veins
- The formation of blood clots, as a result of stagnation of blood in the veins;
- detachment of thrombus and occlusion of the vessel coincides with its diameter;
- thrombophlebitis (clot formation in the lumen of the vein it is inflammation of the walls);
- pulmonary embolism (detached blood clot in the blood gets into the pulmonary artery, which participates in blood circulation in a small circle. If the clot diameter coincides with the diameter of the trunk of this artery, it can cause sudden death. If the clot is smaller in diameter, it passes on to the branches of the pulmonary artery, causing pulmonary infarction or edema).
- sores or eczema of the legs caused eating disorders (poor blood circulation leads to lack of oxygen in the tissue, which is the main nourishment of the tissues of the body);
- swelling different areas of the body as a result of stagnation in the veins (they are soft, elastic, bluish in color, their education does not depend on the time of day, often form in the affected area);
- dermatitis (skin inflammation in the affected area) due to malnutrition of the site;
- change the color of the skin in the affected area;
- sealing subcutaneous fatty tissue in the affected area due to swelling.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
- The flagellum (functional) tests (determination of the patency of veins and their valves): Troyanova - Trendelenburg,Pratt, Chania, Delbe-pertes and others. One of the most common test Troyanova - Trendelenburg with which the patient being in a horizontal position, lifts the leg at 45 0, the doctor makes a stroking from the foot up (as a result, the superficial veins are emptied), then establishes a tourniquet to the upper thigh and asks the patient to stand normally, the filling of the veins of the lower leg should happen more than 15 seconds;
- Duplex ultrasound scanning of the veins (ultrasound angioscanning) is an informative method, which allows to estimate the blood flow in the vessel and see the vessel;
- Dopplerhophy - the method by which to evaluate blood flow in the vessel;
- Venography is the injection of a contrast agent intravenously and the study of the x-ray picture;
- Phleboscintigraphy - intravenous administration of the radiopharmaceutical and the observation on a special device.
The treatment of varicose veins
Non-surgical treatment

- Traditional methods of treatment (as a complement to medical treatment): wearing compression hosiery (stockings); special exercises (swimming, Cycling, skiing, his legs above his head about 20 0 towards the bed, special exercises ("Bicycle" lying on your back and breathing, imagine that you pedal a Bicycle; alternately bend and unbend the foot at the ankle joint forward and back) are used to enhance the outflow of blood, but not only in complicated cases); contrast shower (under running water to keep feet gradually reducing the temperature of the water reaching the cold); a foot bath (not hot) decoction of oak bark, chestnut, chamomile, St. John's wort; rubbing alcohol tincture of acacia flowers, the leaves of Kalanchoe, Apple cider vinegar; thrombophlebitis treatment with leeches.
- The day: in the morning, slow getting up out of bed (about 5-10 minutes), during sleep puts the cushion under the heel so as to lift the leg approximately 15-20 0 relative to the bed, the walk must be calm, you cannot sit crossed leg on the leg, bandaging the legs with elastic bandages from the foot to upper thigh, wearing medical stockings, good nutrition, to avoid any tedious movements and any substances or factors that contribute to thickening of the blood, with the exception of Smoking, the prevention of constipation.
- Diet : the body needs foods that contain vitamins, strengthen blood vessels and improves blood flow: vitamin C (contained with the citruses, tomatoes, rose hips, etc.), vitamin E (legumes, liver, egg yolk, green onion), vitamin R (grapefruit, walnut, black currant), bioflavonoids (dark sweet cherry, sour cherry), copper (seafood). A sufficient daily amount of fluid at least 1, 5 liters. Limited to the use of alcoholic drinks, coffee, marinades, smoked products.
Surgical treatment
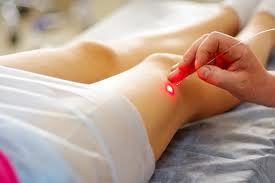
Phlebectomy:Indications for removal veins: extensive varicose veins, saphenous vein pathologically expanded, trophic disorders of the skin, which are not amenable to conservative treatment, acute thrombophlebitis, varicose saphenous veins is accompanied by violation of the General condition (severe fatigue, swelling of the legs) of the patient. Contraindications to the removal veins: coronary heart disease, a serious infectious processes, the older age of the patient, pregnancy in 2nd and 3rd trimesters, inflammation on the legs (erysipelas, pyoderma, eczema). The advantages of surgical treatment: the only treatment in severe cases, the only radical method of correction of the valves of the deep veins. Disadvantages of surgical treatment: traumatic (cosmetic defect), requires anesthesia, you need is a few days in the hospital under the supervision of the surgeon. Laser therapy (endovascular microtermocoagulation) :Indications: a Combination of varicose veins with the following diseases: diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary heart disease, high blood pressure), peripheral vascular disease (phlebitis, thrombophlebitis), respiratory diseases (asthma, bronchitis, pleurisy), with diseases of the digestive system (cholecystitis, peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer), diseases of the nervous system (craniocerebral traumas, neuroinfections), diseases of the genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, endometritis, salpingitis), with skin diseases (dermatitis, Neurodermatitis), peritonitis, boils. Contraindications: people suffering from oncological diseases, diseases of the liver, kidneys and heart in the phase of decompensation, cerebral sclerosis, pregnancy. Advantages: eliminates unpleasant vascular pattern, a quick procedure (15-20 min), requires no hospitalization, safe and painless, does not injure the vessel tissue and surrounding tissue. Disadvantages: not available everywhere method expensive method, removing the larger vessels possible thermal tissue damage, possible formation of scars and depigmentation (whitening) of the skin in the treated area. Radiofrequency coagulation (ablation) of varicose veins: Indications: varicose veins with a lesion of the trunk of great and small saphenous veins, trophic ulcers as a result of varicose veins. Contraindications: acute thrombophlebitis of subcutaneous veins, the impossibility of active walking, pregnancy, mental disorder. Advantages: no cosmetic defect, painless, requires no hospitalization, does not violate the capacity. Drawbacks: the only drawback is the price. Sclerotherapy: Indications: small varicose veins, large varicose veins when using duplex dopplerography, varicose veins in the early stages (if the damage is only superficial veins. Contraindications: pregnancy and breast-feeding, allergic to sclerosus, deep vein thrombosis, purulent-inflammatory diseases of the feet. Advantages: lower cost compared to surgery, a quick period of restoration, does not require stay in hospital (to go home), the best cosmetic result. Disadvantages:possible uptake in the deep vein sclerosus, decreased efficiency due to the mixing sclerosus with blood, are ineffective in advanced cases.




































